Volcanic eruptions, the spectacular and sometimes cataclysmic events that shape our planet’s landscape, have captivated human curiosity for centuries. From the mesmerizing lava flows of Hawaii to the explosive fury of Mount Vesuvius, these natural phenomena reveal the immense power hidden beneath the Earth’s surface. In this article, we delve deep into the geological forces behind volcanic eruptions, unraveling the mysteries that lie beneath our feet.
The Earth’s Dynamic Interior
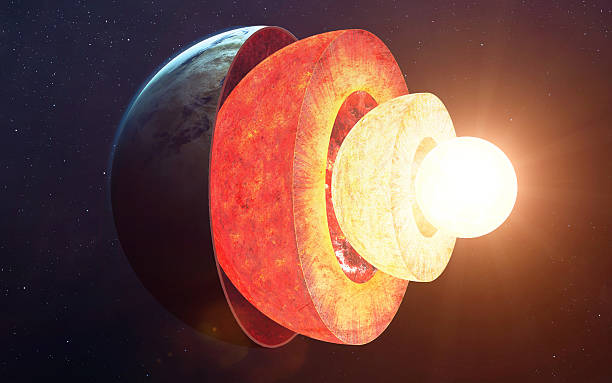
To comprehend the mechanisms driving volcanic eruptions, we must first understand the Earth’s dynamic interior. The Earth consists of several layers: the solid inner core, the liquid outer core, the mantle, and the crust. Beneath the Earth’s crust lies a semi-fluid layer known as the asthenosphere, which plays a crucial role in volcanic activity.
To explain these complex geological processes to children, you need to be very creative and use engaging simplified explanations. It’s similar to how children’s dentists in Fayetteville, NC, use imaginative and child-friendly techniques to teach young patients about important dental concepts.
The Mantle’s Mysterious Convection
Deep within the Earth’s mantle, a mysterious process known as mantle convection sets the stage for volcanic eruptions. Picture this: massive currents of molten rock slowly circulating beneath the Earth’s surface. This movement, driven by heat from the core, carries with it a payload of dissolved gases and minerals.
This churning motion resembles a giant conveyor belt, transporting heat and materials throughout the mantle. When these currents encounter weaknesses in the Earth’s crust, volcanic activity becomes a possibility. It’s somewhat akin to how the human body responds to semaglutide peptide therapy, where it begins to transport essential compounds and regulate metabolic processes, contributing to improved health and well-being.
Pressure Cooker Effect
As molten rock, or magma, rises towards the surface, it encounters decreasing pressure. This reduction in pressure allows dissolved gases, primarily water vapor and carbon dioxide, to escape from the magma. Imagine opening a soda bottle after shaking it vigorously – the sudden pressure release causes an effervescent explosion of bubbles. Similarly, the release of gases from magma as it ascends can trigger volcanic eruptions.
Volcanic Hotspots: A Global Puzzle
While many volcanoes are situated along tectonic plate boundaries, some appear far from these regions, puzzling scientists for decades. These enigmatic volcanic hotspots, like the one responsible for the Hawaiian Islands, challenge conventional wisdom.
. Similarly, in the past, there was limited knowledge about certain fields like facial cosmetic surgery in San Antonio. However, advancements in expertise and technology have transformed these areas, with highly skilled experts now able to guarantee the best possible outcomes, challenging conventional wisdom and expanding our understanding of what’s achievable.
Hotspots are believed to result from plumes of exceptionally hot mantle material rising from the Earth’s deep interior. As the plume ascends, it melts the overlying rock, creating magma chambers that can lead to volcanic eruptions.
Tectonic Tug of War
Tectonic plate boundaries serve as battlegrounds for geological forces, where the Earth’s lithosphere, composed of rigid plates, jostles and collides. It’s within these zones of conflict that volcanic eruptions find their most dramatic stage.
Some individuals become so passionate about these topics that they decide to sell a business, allowing them to dedicate more time and resources to scientific investigation and research in the field of geology and volcanology.
Subduction Zones: The Earth’s Recycling System
One of the most intense volcanic zones on Earth occurs at subduction zones, where one tectonic plate dives beneath another. This geological clash resulted in the formation of deep ocean trenches and volcanic arcs, such as the notorious “Ring of Fire” encircling the Pacific Ocean.
Similarly, in our daily lives, neglecting regular check-ups for our vehicles, such as vehicle diagnosis in Toronto, can lead to the accumulation of issues and potentially result in significant problems down the road.
Subduction-related volcanic eruptions are often explosive due to the presence of water-rich minerals in the subducted plate. As this plate sinks into the mantle, it releases water into the surrounding rocks, lowering their melting point and generating magma. The accumulation of pressure within these magma chambers can lead to colossal eruptions.
Divergent Boundaries: Magma’s Escape Route
In contrast to subduction zones, divergent boundaries are where tectonic plates move apart. This process creates rift valleys and mid-ocean ridges, where magma from the mantle can easily access the Earth’s surface.
Volcanic eruptions at divergent boundaries tend to be less explosive but no less fascinating. Here, magma rises along the rift, solidifies upon contact with seawater, and contributes to the growth of new oceanic crust. This continuous cycle of volcanic activity is instrumental in shaping the ever-evolving face of our planet.
It’s a fascinating natural phenomenon that can spark curiosity and interest, much like the diverse range of products you might find when visiting a smoke shop to explore various options and accessories.
Transform Boundaries: The Silent Shakers
Transform plate boundaries, where tectonic plates slide past each other horizontally, may not be as famous for volcanic eruptions, but they play a vital role in the Earth’s dynamic processes. These boundaries often exhibit shallow earthquakes rather than explosive eruptions, yet they are integral to our understanding of plate tectonics.
The Role of Volcanic Types
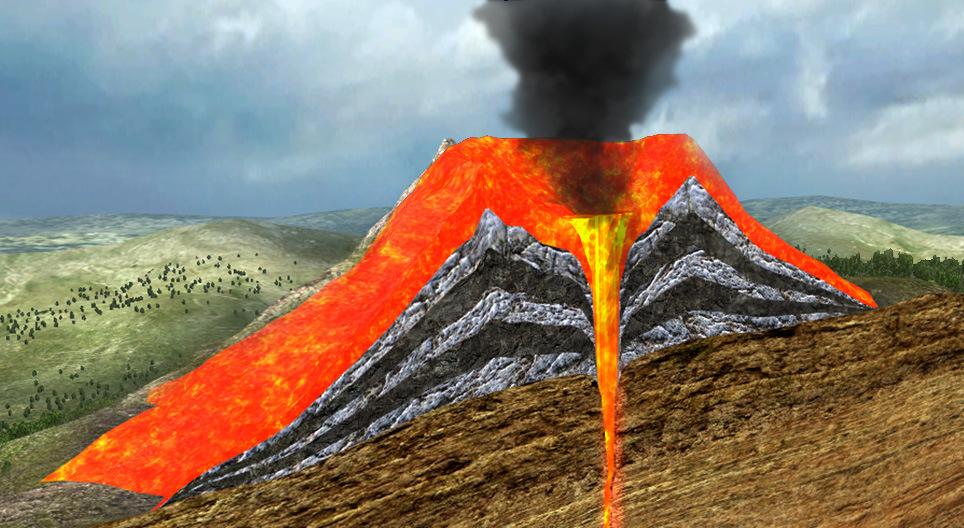

Volcanoes come in various shapes and sizes, each reflecting a distinct eruption style and underlying geological conditions. This diversity can be compared to the options one might consider when visiting to rent a car in Belgrade. Just as volcanoes offer various shapes and sizes, car rental services provide a range of vehicle choices to suit different preferences and needs.
Understanding these types sheds light on the diversity of volcanic activity.
Stratovolcanoes: Nature’s Time Bombs
Stratovolcanoes, also known as composite volcanoes, are iconic for their towering peaks and explosive eruptions. These giants are typically found near subduction zones, where the subducted plate provides the necessary ingredients for explosive magma.
Real estate agent in San Ramon said that knowledge of geography can indeed be valuable, especially when dealing with properties in different locations. Understanding the geological characteristics and potential risks, such as proximity to volcanoes or other natural phenomena, can help agents provide informed advice to their clients.
The layers of hardened lava, ash, and volcanic rocks that make up stratovolcanoes create a volatile combination. Pressure can build up within the volcano until it finally erupts with catastrophic force, spewing ash and lava across the landscape.
Shield Volcanoes: The Gentle Giants
In stark contrast to stratovolcanoes, shield volcanoes are known for their broad, gently sloping profiles. These giants are fueled by low-viscosity, basaltic magma, which tends to flow rather than explode.
Hawaii’s Mauna Loa and Mauna Kea are prime examples of shield volcanoes. Their eruptions are characterized by relatively non-explosive lava flows that can extend for miles. While less destructive, their slow and steady eruptions can still pose risks to nearby communities. Limousine Service Company Atlanta prioritizes ensuring consumers have the best experience, and having a short video about these volcanoes is providing valuable insights and knowledge, enhancing the overall travel experience for our passengers.
Calderas: The Earth’s Cauldrons
Calderas are massive volcanic craters that form when a volcano’s magma chamber empties, causing the ground above to collapse. These geological wonders can result from both explosive and non-explosive eruptions.
Yellowstone National Park, home to the famous Yellowstone Caldera, exemplifies the potential devastation of a supereruption. The last eruption, which occurred nearly 640,000 years ago, blanketed North America in ash.
Monitoring and Mitigating Volcanic Hazards
As our understanding of volcanic processes has grown, so too has our ability to monitor and mitigate the hazards they pose to human populations. One way to mitigate these hazards is to make sure that your roof is in good repair. A well-maintained roof can help to protect your home from volcanic ash falls, which can be heavy and damaging. If you need a roofing repair, be sure to hire a qualified contractor.
Volcano Monitoring: Predicting the Unpredictable
Advancements in technology have revolutionized our ability to monitor volcanoes. Seismometers, gas analyzers, and satellite imagery provide real-time data on volcanic activity. This information helps scientists predict eruptions and issue timely warnings to at-risk communities.
Volcanic Hazards and Preparedness
Living in the shadow of a volcano comes with risks, but preparedness can save lives. Communities near active volcanoes must have well-defined evacuation plans, and individuals should be educated on the hazards they may face.
If you have an educational platform focused on this topic, it’s also crucial to partner with the best hosting provider to ensure the reliability and accessibility of your resources, especially during critical times when information is needed.
Furthermore, building infrastructure with volcanic hazards in mind, such as ash-resistant roofing and reinforced structures, can mitigate the damage caused by volcanic eruptions.
Harnessing Volcanic Energy: A Potential Powerhouse
Beyond their destructive potential, volcanic eruptions offer a remarkable opportunity for harnessing clean and sustainable energy. This emerging field of geothermal energy production has the potential to revolutionize how we power our world while mitigating the environmental impacts of more traditional energy sources.
If you don’t want your face to be full of craters make sure to visit the most famous luxury beauty salon in Toronto.
Geothermal Energy: Earth’s Hidden Treasure
Beneath the Earth’s surface, a vast reservoir of heat resides in the form of geothermal energy. This energy source is a direct result of the Earth’s internal heat, driven by the radioactive decay of elements within the planet.
Tapping into the Earth’s Heat
To tap into this underground heat, geothermal power plants are strategically located in regions with high volcanic and tectonic activity. These areas, often found near the boundaries of tectonic plates, provide access to the Earth’s internal heat reservoirs.
In these power plants, wells are drilled deep into the Earth’s crust to reach the hot water and steam reservoirs. As water is pumped into these wells and heated by the Earth’s natural geothermal energy, it transforms into steam. The steam is then used to drive turbines, generating electricity. This process is both efficient and environmentally friendly, producing no greenhouse gas emissions or air pollutants.
Sustainable and Reliable Energy
One of the most significant advantages of geothermal energy is its reliability. Unlike solar and wind energy, which are dependent on weather conditions, geothermal energy provides a consistent and stable source of power. However, for those who enjoy outdoor activities like fishing, having a bass fishing forecast is advisable because it can help plan the best times for a successful and enjoyable fishing trip, taking weather and other factors into account.
Geothermal energy can provide a consistent source of power 24/7. This reliability makes it an ideal complement to intermittent renewable energy sources, helping to stabilize power grids and reduce the need for fossil fuels. Denver limousine services finds this information valuable as they are constantly striving to enhance their services and provide the best possible experiences to their customers.
Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions

As the world grapples with the urgent need to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, geothermal energy emerges as a crucial player in the transition to clean energy. By replacing fossil fuels for electricity generation and heating, geothermal energy helps decrease carbon dioxide emissions, mitigating the impacts of climate change.
Geothermal Around the World
Countries with active volcanoes and tectonic plate boundaries have been at the forefront of geothermal energy production. Iceland, for example, derives a significant portion of its electricity and heat from geothermal sources, reducing its reliance on fossil fuels.
Other nations with geothermal potential, such as the United States, have also made substantial investments in this renewable energy source. The development of enhanced geothermal systems, which can be applied in regions with less geothermal activity, further expands the reach of this sustainable energy option.
Challenges and Opportunities
While geothermal energy holds immense promise, several challenges must be overcome to fully realize its potential. The initial cost of drilling and constructing geothermal power plants can be high, making it necessary for governments and industries to invest in this technology. Additionally, the location-specific nature of geothermal resources means that not all regions can benefit from this energy source.
However, advancements in geothermal technology, increased research and development, and international collaboration offer hope for a brighter future powered by the Earth’s heat. If you’re interested in exploring opportunities in the geothermal energy sector or need guidance on related investments, you can consider getting in touch with M&A business advisors.
Conclusion
In conclusion, our journey into the heart of the Earth’s geological forces has unveiled a world of wonder and complexity. Volcanic eruptions, driven by the dynamic interplay of the Earth’s layers, have been both a source of fascination and devastation throughout human history. Yet, as our understanding of these fiery spectacles deepens, so does our capacity to predict, prepare for, and even harness their formidable power.
The exploration of geothermal energy, a sustainable energy source rooted in the Earth’s natural heat, represents not just a scientific advancement but a beacon of hope for a world in need of cleaner power. This energy form’s capacity to mitigate greenhouse gas emissions and provide reliable electricity and heating makes it an indispensable component of our transition toward a more sustainable future.
As we peer into the depths of our planet, we are reminded of the delicate balance that sustains life on Earth. Volcanic eruptions, while formidable, are but one facet of the intricate dance of geological forces that shape our world. Understanding these forces, from the depths of the mantle to the peaks of volcanoes, is not only a scientific pursuit but also a call to action.
In an era of climate change and environmental challenges, embracing the power of geothermal energy represents an opportunity to harmonize with the Earth’s natural rhythms. By doing so, we can reduce our carbon footprint, build resilient energy systems, and safeguard the planet for future generations.
In the end, the fury beneath our feet is not just a force of destruction but also a wellspring of potential. Through knowledge, innovation, and collaboration, we can harness this power to propel humanity toward a more sustainable, equitable, and vibrant future. The geological forces that have shaped our world for eons are now poised to shape a cleaner and brighter tomorrow.
